Parallel Circuits
A parallel circuit is one in which current can flow through several paths simultaneously.
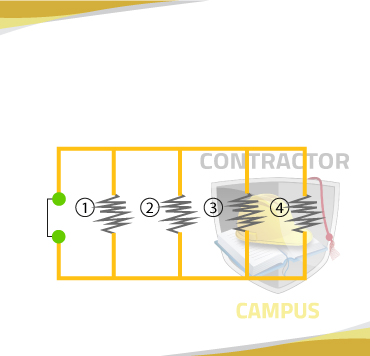
Notice that unlike a series circuit in this circuit current flows through resistors 1, 2, 3 and 4 simultaneously.
If you stopped the flow of current at any of those resistors, current would still flow through the others. See circuit this concept.
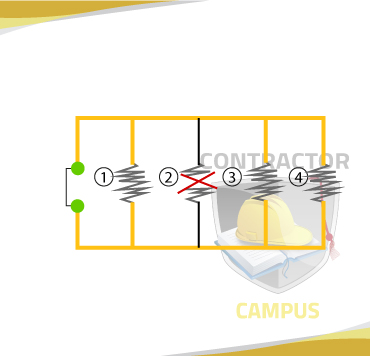
Parallel Circuit Rules and Formulas
Total Voltage is the same or the voltage on any resistor. The voltage on all resistors is the same.
Total Voltage = Voltage at resistor 1 = ...Voltage at Resistor n
Vt = V1 + V2 + ... Vn
Total Current is the sum of the individual currents on the different resistors.
Total Current = Current at resistor 1 + Current at resistor 2 + ... Current at Resistor n
It = I1 + I2 + ... In
Total Inverse Resistance is equal to the sum of the inverses of the individual resistances
Total Inverse Resistance = Inverse Resistance 1 + Inverse Resistance 2 + ... Inverse Resistance n
Example 1:
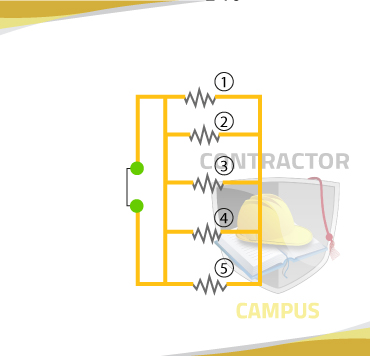
What's the total current and total Voltage for the circuit below?
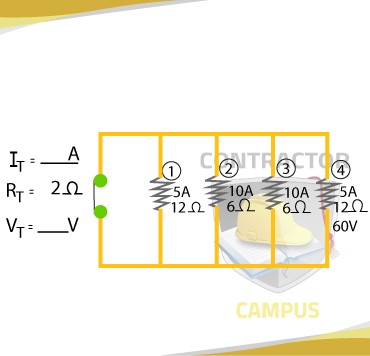
It = I1 + I2 + I3 + I4
It = 5A + 10A + 10A + 5A
It = 30A
It = 5A + 10A + 10A + 5A
It = 30A
Since Voltage is the same everywhere in a parallel circuit, the total voltage must be 60V.
Example 2:
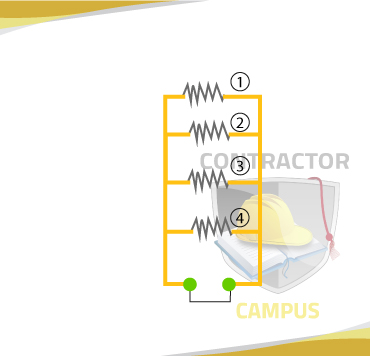
What's the total resistance of the circuit below? There are two ways of solving this problem.
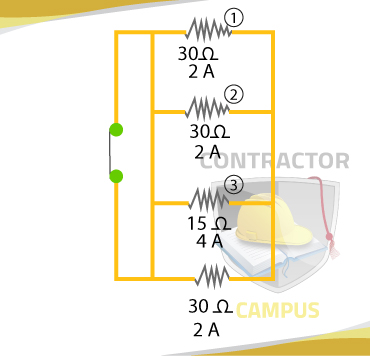
You can use the formula for the total resistance.
1/Rt = R1 + V2 + R2 + R3 + R4
1/Rt = 1/30 + 1/30 + 1/15 + 1/30
1/Rt = 1/30 + 1/30 + 1/15 + 1/30
To add fractions, I must find a common denominator. In this case, it is 9. We know that because 60 is divisible by 4, 12, 30, and 4.
1/Rt = 1/30 + 1/30 + 2/30 + 1/30
Notice the third fraction becomes 2/30 instead by 1/30 in order for all fractions to have a common denominator.
1/Rt = 5/30
Now, divide both the numerator and the denominator by a number that will turn the numerator into a 1. Let's divide both numbers by 3.
1/Rt = 5 ÷ 5 / 30 ÷ 5 = 1/6
1/Rt = 1/6
Rt = 6
1/Rt = 1/6
Rt = 6
Another way of nothing this problem is by using the circuit totals and using ohm's law
First, we calculate the circuit's total current
It = 2A + 2A + 4A + 2A
It = 10A
It = 10A
Then, we calculate the circuit's total voltage. If we calculate the voltage at any resistance, that will be the total voltage. Let's do it on the first resistance.
V1 = I1 x R1
V1 = 2A x 30 Ω
V1 = 60V
Vt = V1 = ... Vn
Vt = 60V
V1 = 2A x 30 Ω
V1 = 60V
Vt = V1 = ... Vn
Vt = 60V
Now that we know
RT = VT / IT
RT = 60V/10A
RT = 6 Ω
RT = 60V/10A
RT = 6 Ω


Comments